introduce
The pH value of waterborne products is of decisive importance to product performance and durability.
1 range
This document specifies a method for laboratory measurements of the pH values of polymer dispersions and coating materials using a pH electrode with a glass film. ISO 19396-2 specifies a method for measuring pH using a pH electrode using ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (ISFET) technology.
2 Normative references
The following files are referenced in the text in such a way that some or all of the content constitutes the requirements of this document. For dated references, citation-only versions apply. For undated references, the latest version of the reference (including any revisions) applies.
ISO 1513, Paints and varnishes – Examination and preparation of test samples
ISO 4618, Paints and varnishes — Terms and definitions
ISO 15528, Paints, varnishes and raw materials for paints and varnishes — Sampling
ISO 80000-9:2009, Quantities and units — Part 9: Physical chemistry and molecular physics
3 Terms and Definitions
For the purposes of this document, the terms and definitions given in ISO 4618 and ISO 80000-9 and the following provisions apply.
3.1 pH
Measurement of acidic or basic reactions in aqueous solutions or polymer dispersions
Note 1: Representation of pH: p and H are perpendicular to a line. The same applies to pOH.
Note 2 Acidic reactions are determined by the activity of existing “hydrogen ions”. The basic reaction is determined by the activity of existing hydroxide ions. The direct relationship between the activity of “hydrogen ions” and hydroxide ions is described by the ionic products of water.
3.2 pH value
Hydrogen ion activity times the interdecadal log of (−1)

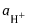 | e activity of hydrogen ions in moles per kilogram; |
| Meter 0 | is the standard molar concentration (1 mole per kilogram); |
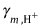 | is the standard molar concentration (1 mole per kilogram); |
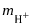 | It’s the molar concentration of hydrogen, in moles per kilogram. |
Note 1: pH cannot be measured as a measure of the activity of a single ion. Therefore, determine the pH (PS) value of the principal reference substance (PS, en: principal standard) solution, which approximates it and can be attributed to it. This is based on a global agreement; See ISO 80000-9:2009, Appendix C.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.2]
3.3 Shaped effect tube electrode
Combined pH electrode using ISFET technology
Potential cells provide voltage depending on the pH of the measured medium (3.2)
Note 1: One of the two electrochemical cells is ISFET; The second is the reference electrode.
Note 2: Integrated temperature sensors are recommended (see Figure 1).
Figure 1 — ISFET electrode design (schematic diagram)

| 1 | Reference electrode, consisting of 2, 3 and 4 | 7 | Open the measuring medium (gate) |
| 2 | Reference Element | 8 | Temperature sensor |
| 3 | Reference electrolyte proportional voltage | at | pH value |
| 4 | Diaphragm | UDS | Voltage Receiver/Transmitter (drain/source) |
| 5 | pH measuring electrode, consisting of 6 and 7 | IDS | current receiver/transmitter (drain/source) |
| 6 | Ion field effect tube (see Figure 4) |
3.4 Reference electrode
The electrode provides a constant potential independent of the pH of the measured medium (3.2)
Note 1: Currently, the most commonly used type is the silver/silver chloride reference electrode, whose potential is stabilized by a constant concentration of potassium chloride (KCl) (3.6) in the reference electrolyte.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.5]
3.5 Referencing Elements
The galvanic cell is immersed in the reference electrolyte (3.6) and transmits the reference potential to the pH meter
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.6, modified — Entry note 1 deleted.
3.6 Reference electrolyte
The potential of the reference electrode is determined by the activity of chloride ions in aqueous and salt solutions (generally potassium chloride solutions) (3.4).
Note 1: At the diaphragm (3.7), the reference electrolyte is in contact with the measurement solution. Potassium chloride solution is used as a reference electrolyte because K+ ions and Cl− ions have nearly identical ionic mobility and therefore produce only a slight diffusion potential.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:17,000, 3.7, modified — Entry note 2 has been deleted.
3.7 Diaphragm
The penetration material (3.4) on the side of the reference electrode housing enables electrolytic contact between the reference electrolyte (3.6) and the measured solution, while impeding electrolyte exchange
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.8, modified — Entry note 1 has been deleted.
3.8 Measuring Electrodes
Ion sensitive field effect transistor
International field effect tube
The electrode provides a pH ratio signal through a suitable electronic circuit
3.9 Temperature Compensation
Only the temperature dependent measurement signals of buffer solutions (3.13) with known temperature dependence are compensated
Note 1: In this way, the temperature dependence of the pH (3.2) of the measured medium cannot be compensated. Therefore, temperature is always recorded along with pH.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.11]
3.10 Theoretical slope k
Variation of pH electrode voltage with temperature

| T | Is the thermodynamic temperature, measured in Kelvin (measuring temperature in °C + 273,15 °C); |
| R | the gas constant 8,314 J mol−1 K−1; |
| F | Faraday’s constant 96, 485 C moles −1. |
Note 1 At 23 °C, k = − 58,57 mV.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.12]
3.11 Practical grade k ‘
The slope of the pH electrode was obtained by measuring the pH proportional voltage of the pH electrode in at least two reference buffer solutions (3.13).

Note 1: The slope obtained during calibration is a feature of the pH electrode quality.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.13]
3.12 Zero Point
The pH value of the pH electrode is (3.2), pH 0, and the pH proportional voltage of the pH electrode is U =0 mV at a given temperature
Note 1 The zero point of the ISFET electrode (3.3) is set by adjusting the offset voltage.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.14, modified — Entry note 1 has been replaced and entry note 2 deleted.
3.13 Buffer solution
pH (3.2) is the solution for which the measurement uncertainty is known
Note 1: Buffer solution is used for PH meter calibration and adjustment. The pH of the buffer solution is essentially insensitive to dilution and acid or base addition.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.15]
3.17 Stability of measured values
Measure the change of the signal with time, dU/dt, under constant measurement conditions
Note 1: The stability of the measurements is specified according to the reproducibility requirements of the measurements.
[Source: ISO 19396-1:2017, 3.16]
Only the standard information section is public. To see the full content, you need to purchase the standard through the official channels.
